Motor Configuration
The R-LINK Configuration Tool is used to configure the AK80-6 from T-Motors. Before starting to use the R-Link device make sure you have downloaded the CP210x Universal Windows Driver from silabs. If this isn’t working properly follow the instructions at sparkfun on how to install ch340 drivers. You have to download the CH 341SER (EXE) file from the sparkfun webpage. Notice that you first have to select uninstall in the CH341 driver menu to uninstall old drivers before you are able to install the new driver. The configuration tool software for the R-LINK module can be downloaded on the T-Motors website.
Tutorials
UART Connection: R-Link module
R-LINK is a USB to serial port module, specially designed for CubeMars A Series of dynamical modular motors. It is possible to calibrate the encoder in the module, change CAN ID settings, PID settings, as well as to control position, torque and speed of the motor within the configuration software tool.
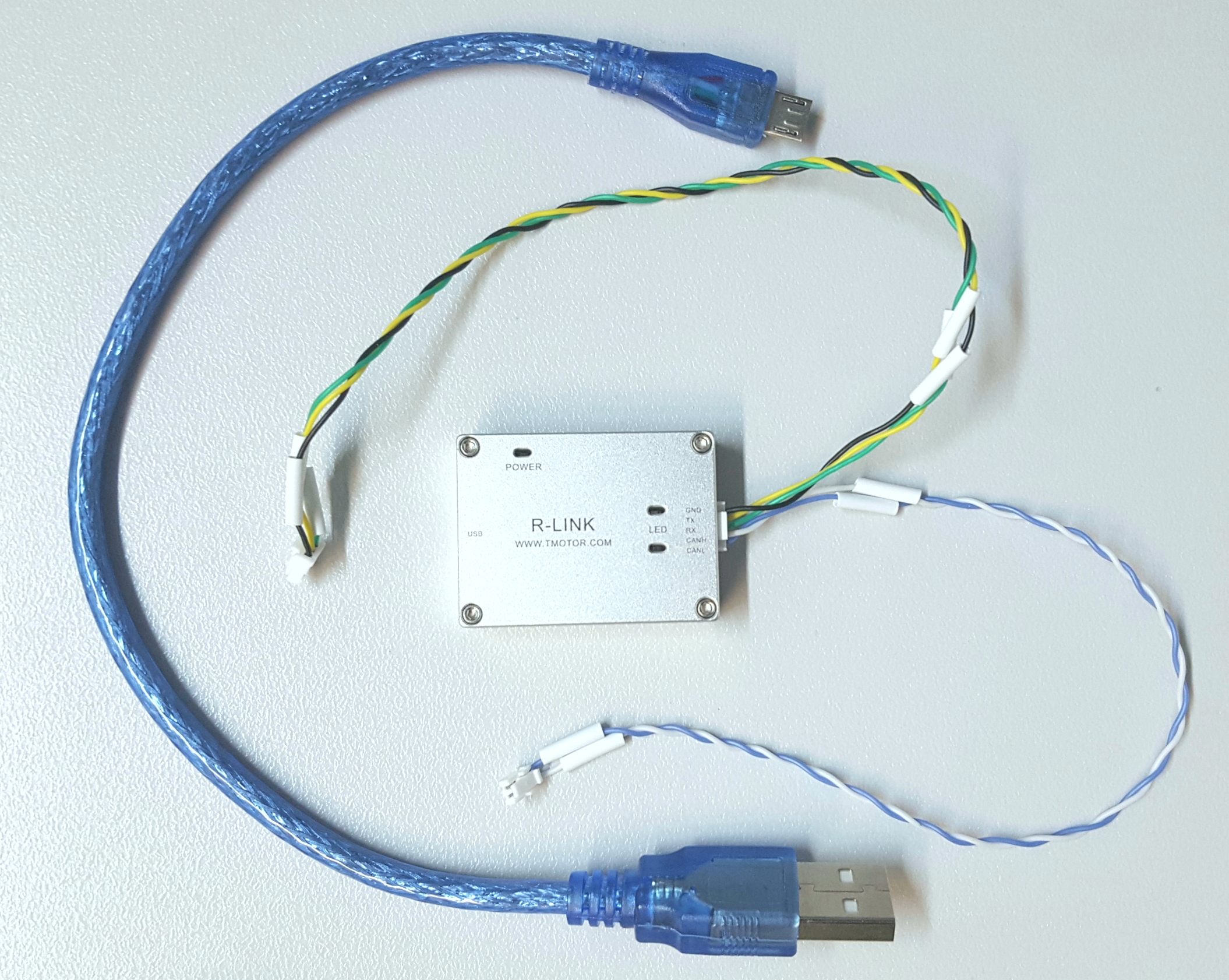
Instructions: R-Link Config Tool
User manual & configuration tool: store-en.tmotor.com
Wire the R-LINK module as shown in the figure below. A USB to micro USB cable connects a pc with the R-LINK module and the 5pin cable goes between the R-LINK module and the Motor.
Connect the AK80-6 motor to a power supply (24V, 12A) and do not cut off the power before the setting is completed. <br/>
Start the R-Link Config Tool application (only runs on Windows).
Select serial port: USB-Serial_CH340, wch, cp along with an appropriate baud rate (both 921600 and 115200 Bd should work). If the serial port option USB-Serial_CH340,wch,cp does not show up, your pc can’t establish a connection to the R-LINK module due to remaining driver issues.
Choose the desired motor settings on the left side of the config tool GUI. Enter the correct CAN ID of the motor under MotorSelectEnter. A label on the motor shows the ID.
Velocity: 5 rad/s is a relatively slow speed of revolution, hence it offers a good starting point.
Torque: be careful setting a fixed torque, because the friction inside the motor decreases with the speed of revolution. Therefore a fixed torque commonly leads to either no movement at all or accelerates the motor continuously.
Start the plotting by ticking the boxes of position, velocity, torque and select Display
Press
Runto start recording the plots.Enter M_Modeto control the motor. This is indicated by a color change of the plot line, from red to green.In order to push changes in the settings to the motor, press Send Once.
Warning
This button does not work reliably. Usually it has to be activated several times before the setting changes actually apply on the motor.
Stop the motor inside the M-Mode by setting the velocity to 0 and pressing Send Once until the changes apply.
Exit M_Modeto exit the control mode of the motor.Warning
The next time you start the motor control with
Enter M_Modethe motor will restart with the exact same settings as you left the control mode with Exit M_Mode. This is especially dangerous if a weight is attached to the pendulum and the motor control was left with high velocity or torque settings.Use
Stopto deactivate the plotting.
Debugging
Error messages that showed up during the configuration procedure, such as UVLO (VM undervoltage lockout) and OTW (Thermal warning and shutdown), could be interpreted with the help of the datasheet for the DRV8353M 100-V Three-Phase Smart Gate Driver from Texas Instruments:
Datasheet: DRV8353M (on the first Page under: 1. Features)
PD-Controller
A proportional-derivative controller, which is based on the MIT Mini-Cheetah Motor, is implemented on the motor controller board. The control block diagram of this closed loop controller is shown below. It can bee seen that the control method is flexible, as pure position, speed, feedforward torque control or any combination of those is possible.
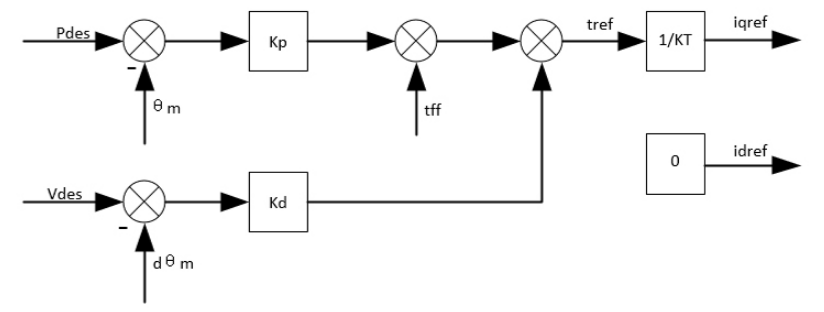
In the motor driver,:
send_rad_command(position_in_radians, velocity_in_radians, Kp, Kd, tau_ff)
lets you set desired position (Pdes), velocity (Pvel), Kp, Kd and feedforward torque (tff) values at every time step.